3D Printed Metals (Additive Manufacturing)
Explore Our 3D Printing Materials
Biodegradable and easy to print; ideal for prototypes and models.
Strong and durable; suitable for functional parts and enclosures.
Combines strength and flexibility; great for mechanical components.
High tensile strength and durability; perfect for industrial applications.
Flexible and elastic; ideal for wearable items and phone cases.
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant; used for automotive and aerospace parts.
High strength and corrosion resistance; suitable for medical and food-grade applications.
Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio; used in aerospace and medical implants.
Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity; ideal for heat exchangers and electronics.
Attractive finish and machinability; commonly used for decorative items.
Imagine a world where you can print anything you need, in any material you want. Where you can create entire objects, from the smallest components to the largest structures, using only a printer.
This is the world of 3D printing.
3D printing is a rapidly growing technology that is being used in a variety of industries, from aerospace to automotive parts. And it's not just limited to making parts and components. 3D printing can be used to create entire finished products, from rocket motors to aircraft components.
3D printing offers a number of advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. It's cheaper, faster, and more flexible. And because it doesn't require any tooling or molding, it's much easier to produce complex or custom shapes.
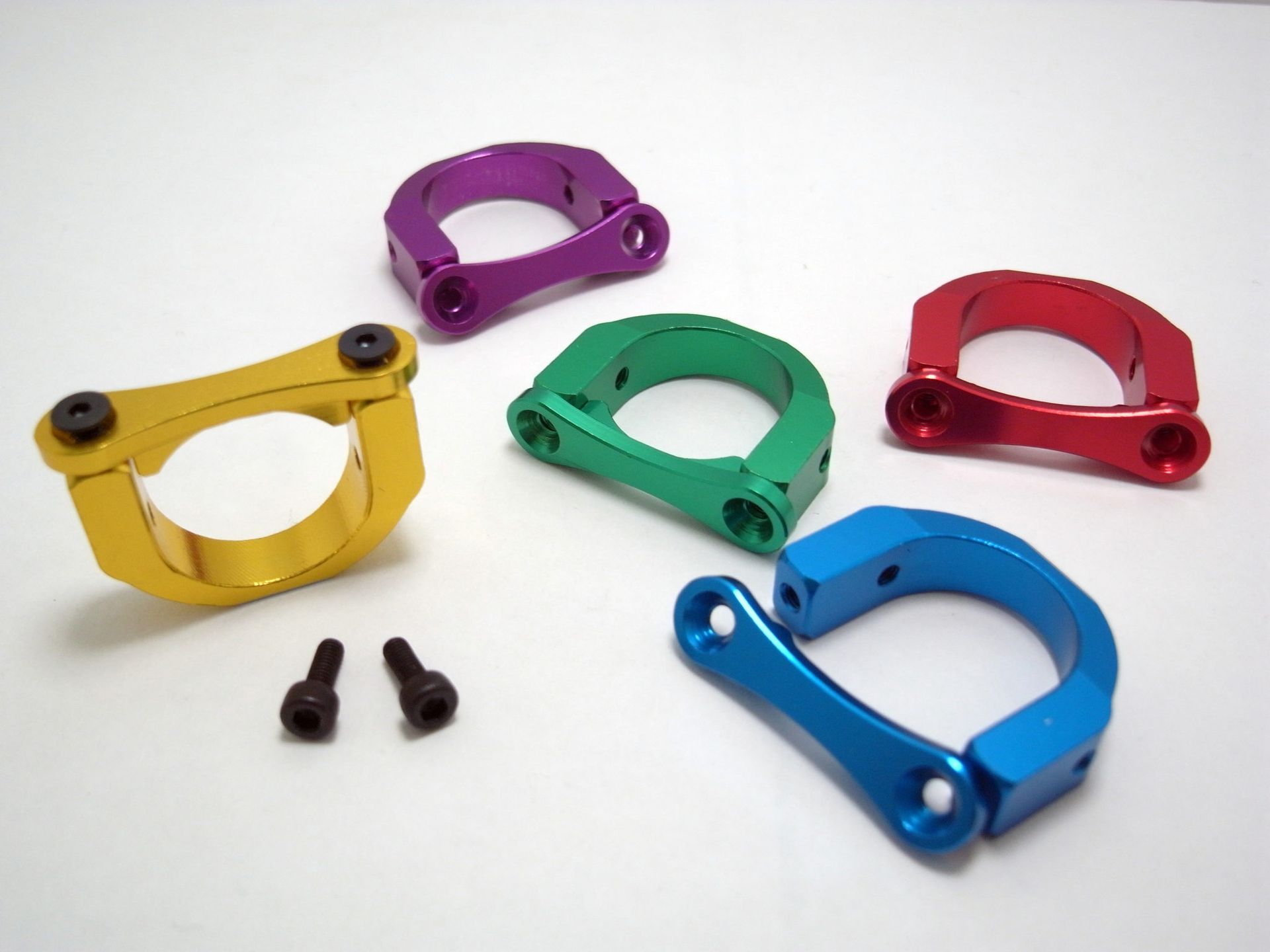
3D printed tool steel, 3D printed Inconel, 3D printed Aluminium, 3D Printed Copper
3D printed metals offer a number of advantages over traditional metals. They're stronger, lighter, and more precise. And because they can be created using less energy and fewer resources, they're more environmentally friendly.
If you can imagine it, you can print it. And with 3D printing, the sky's the limit.
As the demand for larger metal parts grows, the technology has evolved to enable the production of larger components.
Technology adopters have already proved that the quality of metal 3D-printed parts equals, or even exceeds that of conventionally manufactured alternatives. That’s why we increasingly see metal AM parts being used in critical systems like rocket engines, heat exchanges and various turbine parts.
The List of Composite materials used in 3D Printing is large and seems to be developing very quickly as more is understood of the technology and the demand is growing. One of the most popular methods for metal 3D printing is known as selective laser melting (SLM) or direct metal laser sintering (DMLS).
In SLM/DMLS, a high-powered laser is used to fuse together small metal powder particles. The metal powder is melted and then deposited in layers according to the desired 3D geometry.
This process can be used to create very complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to fabricate using traditional machining methods. In addition, SLM/DMLS metal 3D printing offers a high degree of design freedom, as it is not limited by the need to create molds or dies.
As a result, this technology is well-suited for prototyping and low-volume production runs. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using metal 3D printing for large-scale structures such as bridges and buildings. This is possible due to the availability of large-format metal 3D printers that are capable of printing metal components with dimensions measuring up to 6 meters in length.
Frequently asked Questions
The More Common 3D Printed Metals
- Aluminium alloys
- Stainless steel & tool steel
- Titanium alloys
- Cobalt-Chrome superalloys
- Nickel superalloys (Inconel)
- Precious metals
3D printing metals is one of the most popular methods for producing a prototype or production spare part. It is strong and durable, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
Also, metal printing is fast and accurate, making it perfect for prototyping or small-scale production.
The most common metals used in 3D printing are stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. However, there are a wide variety of metal alloys that can be used depending on the specific application. For example, bronze is often used for casting applications, while copper is used for electrical applications.
The list of metal alloys that can be used in 3D printing is constantly expanding as more is understood about the technology. In addition to metal alloys, a variety of other materials can be used in 3D printing, including plastics, resins, and even glass. The type of material that is used will depend on the specific application.
For example, plastic is often used for prototypes because it is relatively inexpensive and easy to work with. However, for final products, metal is usually the best choice because it is more durable and has a higher quality finish.
The list of materials that can be used in 3D printing is constantly expanding as the technology evolves.
Benefits of 3D Printed Metals
- Metal 3D printing processes can be used to manufacture complex, bespoke parts with geometries that traditional manufacturing methods are unable to produce
- Metal 3D printed parts can be topologically optimized to maximize their performance while minimizing their weight and the total number of components in an assembly
- Metal 3D printed parts have excellent physical properties and the available material range includes difficult to process otherwise materials, such as metal superalloys
- Speed to Market
- Cost Saving
- Reduced Carbon Foot print