RAPID PROTOTYPING & SMALL BATCH PRODUCTION
Rapid prototyping serves as an invaluable tool for businesses aiming to swiftly iterate and test their product designs, enabling them to refine concepts and identify improvements efficiently. For small batch production runs, 3D printing technologies (FDM) and (SLS) provide a cost-effective and agile solution, enabling companies to produce limited quantities of customized components or products without the need for expensive tooling or lengthy setup times
Fused Deposition Modeling
or FDM 3D Printing
FDM printers work by heating a thermoplastic filament to its melting point and then extruding it, layer by layer, to create a three dimensional object.
FDM printers are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making them a popular choice for home and small-scale 3D printing
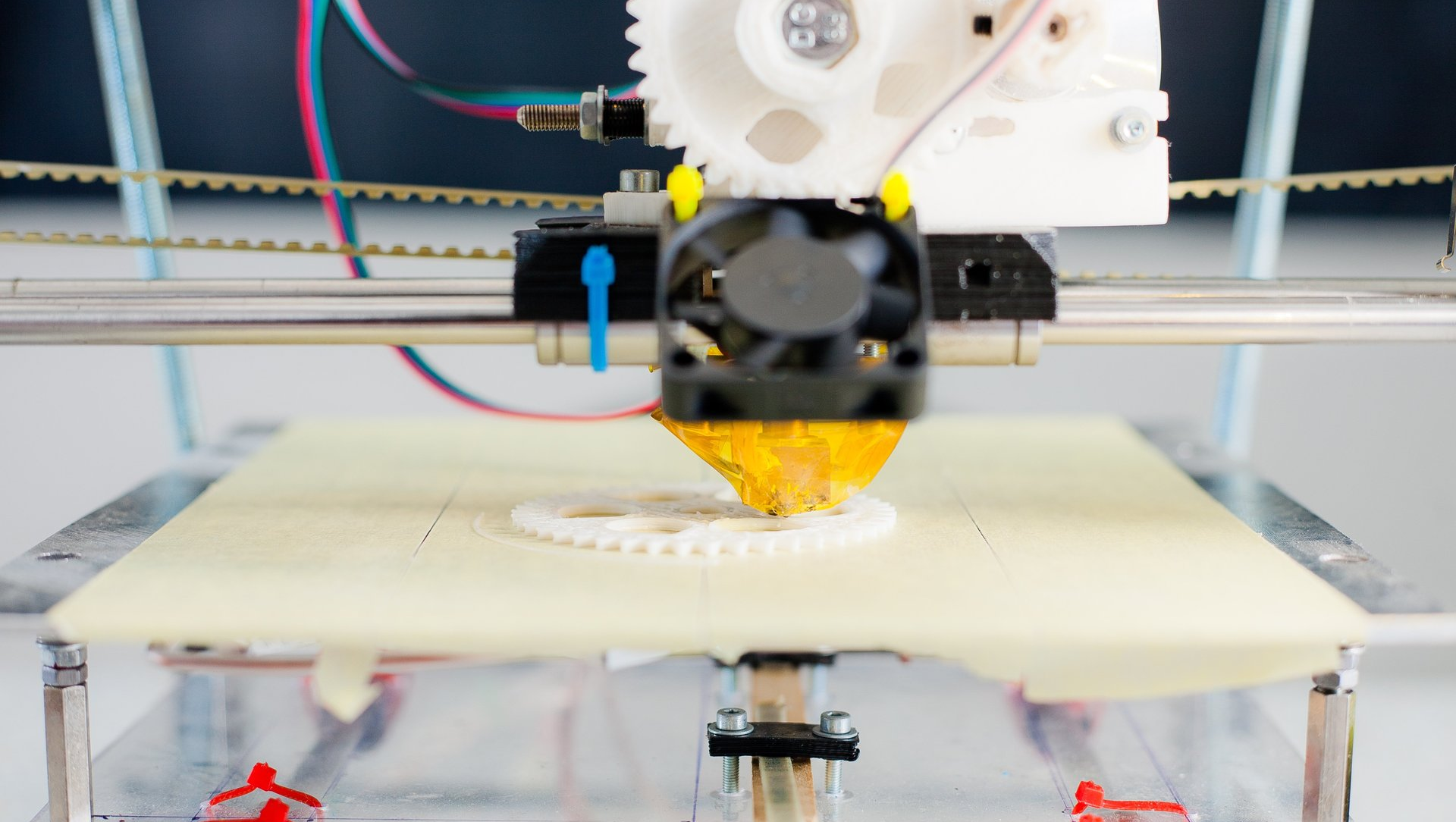

Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography works by using a photopolymer resin that is cured by exposure to light.
The machine traces out the desired geometry layer by layer using a computer-controlled moving laser beam.
The beam is directed by mirrors that are positioned around the build platform.

CAD DESIGN & REVERSE ENGINEERING
When it comes to certain projects, a computer-aided design, or CAD, can be extremely beneficial. A main advantage to using CAD is the fact that it provides experts with greater accuracy. This is done by replacing manual drafting with electronic design software, such as SketchUp, Fusion 360, or AutoCAD Design Edition.
Injection Moulding
Mitchell & Son's mission is to provide access and excellence in production. If your business needs mass production of parts, traditional methods such as injection molding may be the best choice for maximum speed and efficiency.
Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mold. Injection molding can be performed with a variety of materials, including metals, glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and forced into a mold cavity where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, molds are made by a moldmaker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminum, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part.
In modern industry, injection molding is the most common form of plastic processing. It is ideal for producing high volumes of the same object because it is fast and relatively inexpensive. The process is also versatile and can be used to produce a wide variety of parts and products.
Injection molding is a common technique used in mass production around the world. The material is melted at high temperatures, after which the melt is placed in a mold and solidifies into the shape required for production. Once cooled, the frame is ready and usually needs little post-treatment.
This process was invented in the 1870s and has been used extensively in the production of plastics, metals, and other materials. Injection molding is quick, efficient, and relatively cheap, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
There are several steps in the injection molding process:
1. The material is melted at high temperatures.
2. The melt is then injected into a mold.
3. The mold cools and solidifies the material into the desired shape.
4. The mold is opened and the cooled part is ejected.
5. The part is then ready for use, with little or no post-treatment required.
Injection molding is a versatile process that can be used to create a wide variety of parts and products. It is particularly well-suited for mass production and can be used to create parts with intricate details and complex geometries.
Which material is used for molding?
There are hundreds of materials that can be used for injection molding, but the most common ones are thermoplastics. Thermoplastics are plastics that can be melted and reformed multiple times. Injection molding is a process of adding molten plastic into a mold to create a desired shape.
There are many different types of thermoplastics, but the most common ones used in injection molding are polypropylene and polyethylene. Polypropylene is a type of plastic that is strong and durable. It is often used to create packaging and containers. Polyethylene is another type of plastic that is often used to create toys and other objects.
Injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process that can be used to create a wide variety of products. The most common products that are created using injection molding are: packaging, containers, toys, and other objects. Injection molding is a quick and efficient way to create products.
Injection molding is a common technique used in mass production around the world. The material is melted at high temperatures, after which the melt is placed in a mold and solidifies into the shape required for production. Once cooled, the frame is ready and usually needs little post-treatment.
This process was invented in the 1870s and has been used extensively in manufacturing since the early 1900s. Today, injection molding is an essential part of many industries, from medical devices to consumer products. If you're looking for injection molding services, look no further, We have the most advanced machines and years of experience, so you can be sure your project is in good hands!